The technological application in Automatic Concrete Block Making Machine
2025-05-28
The technological applications in an Automatic Concrete Block Making Machine encompass a range of innovations that enhance efficiency, precision, automation, and quality control in the production of concrete blocks. Here's an overview of the major technological applications:
1. Automation and PLC Control Systems
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs): These control systems automate the sequence of operations including material feeding, mixing, molding, and block ejection.
Human-Machine Interface (HMI): Touchscreen interfaces allow operators to control and monitor machine parameters in real-time.
Remote Diagnostics and Control: Some machines support remote operation and troubleshooting via IoT or cloud-based systems.
2. Hydraulic Systems
High-Pressure Hydraulic Systems: Provide uniform pressure for compacting the concrete mix, resulting in high-strength and consistent blocks.
Proportional Valves and Sensors: Enhance the precision of pressure control during block formation.
3. Molding Technology
Vibration + Hydraulic Compression: Combined systems improve the density and surface finish of the blocks.
Interchangeable Molds: Enable quick changes between different block types (hollow, solid, pavers, etc.).
4. Material Handling and Mixing Automation
Automated Batching Systems: Precisely weigh and mix aggregates, cement, and water.
Conveyor Belts and Feeders: Transport raw materials efficiently to the mixer and mold unit.
5. Quality Control and Sensors
Load Cells: Measure the exact weight of materials for consistency.
Moisture Sensors: Detect and control the water content in the mix, crucial for block quality.
Block Dimension and Defect Detection: Vision systems or laser scanners may be used to inspect block uniformity and surface quality.
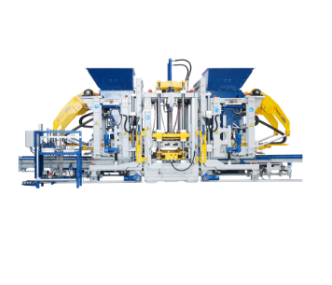
6. Palletizing and Stacking Automation
Robotic Arms or Stackers: Automatically stack finished blocks onto pallets for curing or transport.
Curing Chambers with Sensors: Monitor temperature and humidity to ensure optimal curing conditions.
7. IoT and Smart Monitoring
Real-Time Data Logging: Monitor production metrics, machine health, and downtime.
Predictive Maintenance: Uses sensor data to forecast component wear and prevent breakdowns.
Energy Monitoring: Optimizes power usage to reduce operational costs.
Emerging Technologies
AI-Based Optimization: Machine learning models can optimize mix designs and operation sequences for improved efficiency.
3D Printing Integration: Some advanced systems explore combining traditional block making with additive manufacturing for custom block shapes.
If you are interested in our products or have any questions, please feel free to contact us and we will reply you within 24 hours.